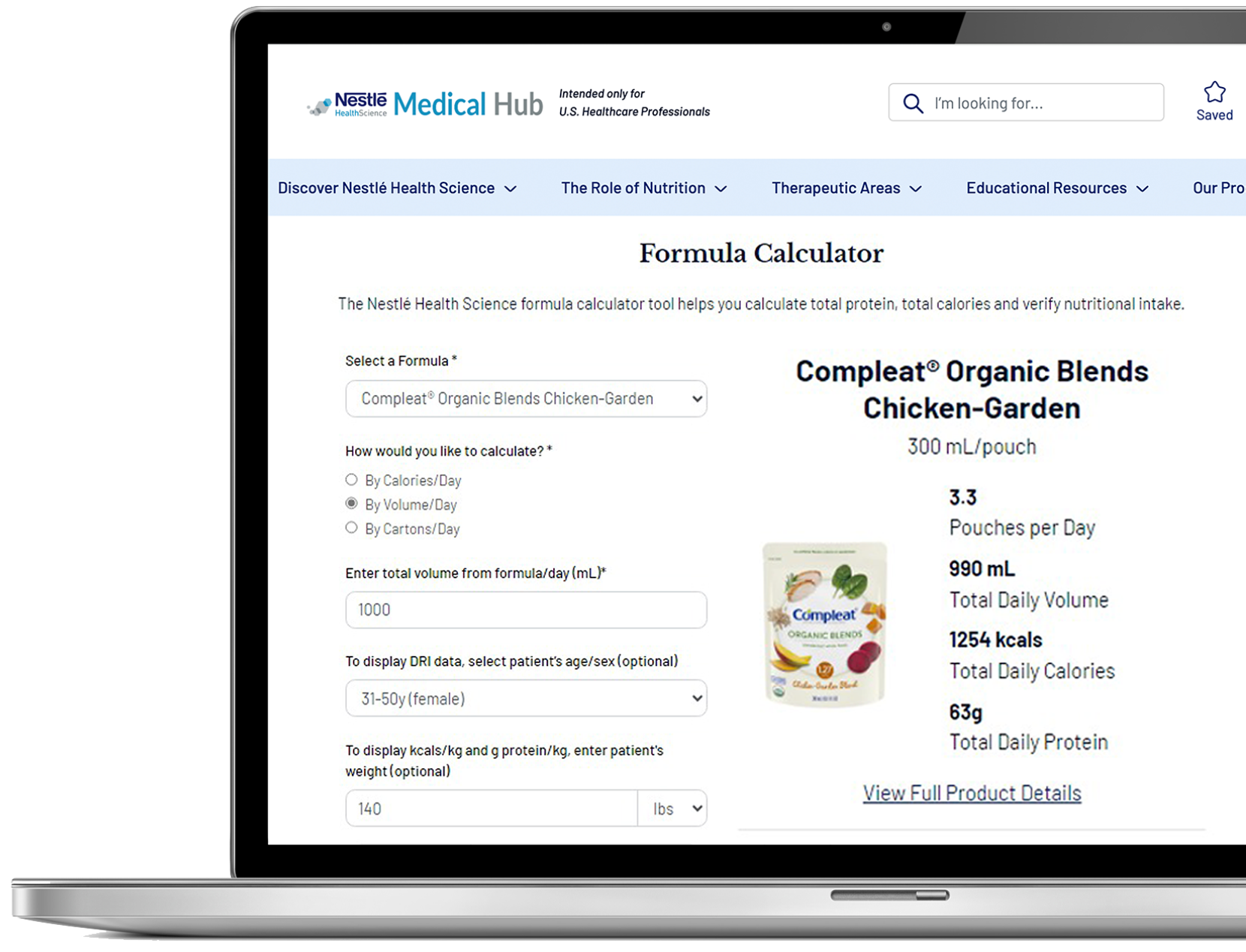
GI Function
Impaired GI Function
Digestive diseases can negatively impact an adult’s gastrointestinal (GI) function. Between 60-70 million Americans are affected by digestive diseases, resulting in 21.7 million hospitalizations per year.1
Impaired GI function significantly impacts the body's capacity to properly digest and absorb nutrients, resulting in malabsorption, malnutrition, and a diminished quality of life.2 This condition is commonly observed in critically ill patients and individuals with chronic GI conditions, and is closely linked to adverse clinical outcomes.3,4 Oral nutrition supplements or enteral nutrition are frequently utilized to deliver essential nutrients and help manage symptoms associated with impaired GI function in adults.
GI Function
Impaired GI Function
Digestive diseases can negatively impact an adult’s gastrointestinal (GI) function. Between 60-70 million Americans are affected by digestive diseases, resulting in 21.7 million hospitalizations per year.1
Impaired GI function significantly impacts the body's capacity to properly digest and absorb nutrients, resulting in malabsorption, malnutrition, and a diminished quality of life.2 This condition is commonly observed in critically ill patients and individuals with chronic GI conditions, and is closely linked to adverse clinical outcomes.3,4 Oral nutrition supplements or enteral nutrition are frequently utilized to deliver essential nutrients and help manage symptoms associated with impaired GI function in adults.
GI Function
> Clinician Tools
- National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Digestive Diseases Statistics for the United States. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/digestive-diseases Last reviewed November 2014.
- Farré R, Fiorani M, Rahiman SA, Gianluca M. Intestinal permeability, inflammation and the role of nutrients. Nutrients. 2020;12,1185. Doi:10.3390/nu12041185. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32340206/
- Reintam Blaser A, Preiser JC, Fruhwald S, et al. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in the critically ill: a systematic scoping review and research agenda proposed by the Section of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Crit Care. 2020. 24: 224. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-02889-4.
- Spiegel BMR, Khanna D, Bolus R, et al. Understanding gastrointestinal distress: a framework for clinical practice. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(3):380-385. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2010.383 https://journals.lww.com/ajg/abstract/2011/03000/understanding_gastrointestinal_distress__a.1.aspx
- Gastrointestinal Complications (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version, National Cancer Institute. Updated May 9, 2023. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/side-effects/constipation/gi-complications-hp-pdq
- Mohamed Elfadil O, Shah RN, Hurt RT, Mundi MS. Peptide-based formula: Clinical applications and benefits. Nutr Clin Pract. 2023 Apr;38(2):318-328. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10961. Epub 2023 Feb 21. PMID: 36802281. https://aspenjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ncp.10961
- Carabotti M, Scirocco A, Maselli MA, Severi C. The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr-Jun;28(2):203-209. PMID: 25830558; PMCID: PMC4367209.
- Nightingale JMD, Paine P, McLaughlin J on behalf of the Small Bowel and Nutrition Committee and the Neurogastroenterology and Motility Committee of the British Society of Gastroenterology, et al The management of adult patients with severe chronic small intestinal dysmotility Gut 2020;69:2074-2092. https://gut.bmj.com/content/69/12/2074
- Samuel J (2022) Brief Note on Functional and Structural Gastrointestinal Disorder. J Hepatol Gastroint Dis. 8:203. https://www.longdom.org/open-access/brief-note-on-functional-and-structural-gastrointestinal-disorder-91249.html
- Berger MM, Hurni CA. Management of gastrointestinal failure in the adult critical care setting. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2022 Apr 1;28(2):190-197. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000924. PMID: 35131994; PMCID: PMC9990607.
- Abrahão V. Nourishing the dysfunctional gut and whey protein. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2012 Sep;15(5):480-4. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e328356b71e. PMID: 22878241.