About Diabetes
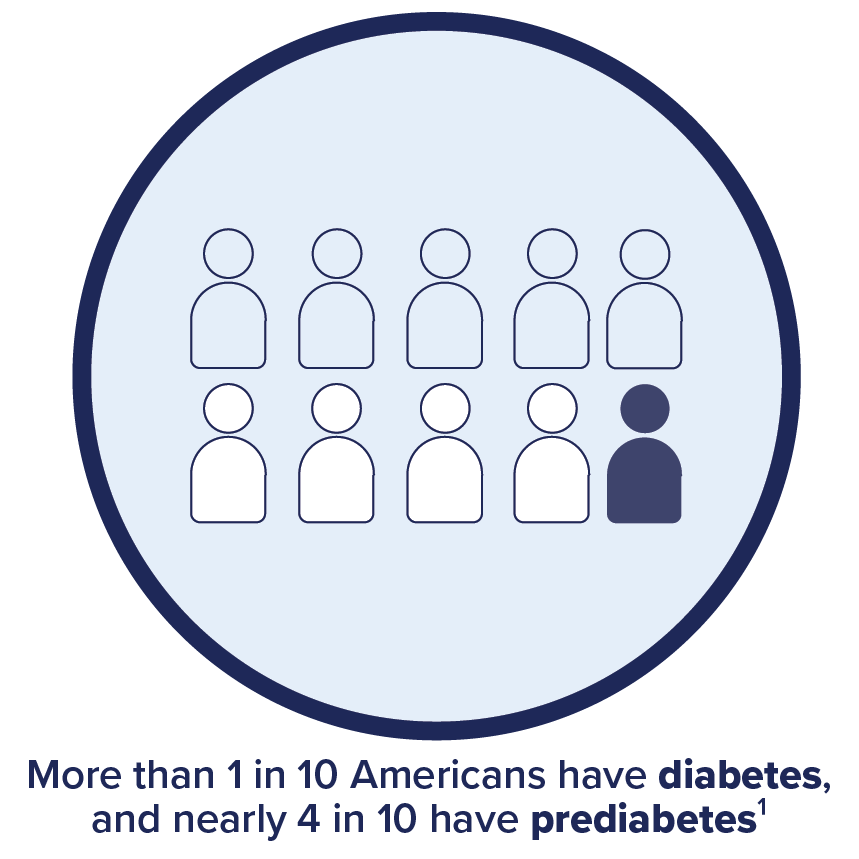
Diabetes impacts everyone – all social, economic, and ethnic backgrounds. In the U.S., it’s estimated that over a third of the adult population (38%) has prediabetes, and more than one in 10 people – have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The majority are diagnosed cases but as many as 8.5 million people are undiagnosed.
Research also shows that the percentage of adults with diabetes increases with age, affecting more than 1 in 4 people aged 65 and older.4 Maintaining steady blood glucose levels is crucial because prolonged hyperglycemia can lead to serious health issues, including cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and renal disease.
Combining weight management with evidence-based nutrition practices not only helps adults with diabetes stabilize their blood glucose levels but also equips those with prediabetes with a strong preventative measure. Regulating carbohydrate intake, through approaches like carb counting, remains a key strategy in managing blood glucose levels. Evidence-based educational resources for both healthcare professionals and patients are also available on our website. Grounded in peer-reviewed research, our nutritional approach aligns with global standards of diabetes care. 3
Nutrition & Diabetes
Nutrition plays a central role in diabetes management due to its direct influence on blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and overall metabolic health. Proper nutrition can help achieve and maintain optimal blood glucose control, reduce the need for medications, minimize the risk of diabetes-related complications, and improve lipid profiles and blood pressure. Also, healthcare professionals can provide individualized nutritional interventions to enhance patient adherence and support better long-term outcomes.2
Nutritional Strategies for Diabetes
Managing the individualized needs of patients with diabetes is important for overall patient health and disease-related outcomes. Embracing targeted nutritional interventions, such as oral nutrition supplements and enteral nutrition, can significantly aid in achieving and maintaining desirable blood sugar levels.
For those patients having difficulty maintaining their nutritional requirements through regular meals and snacks, oral nutrition supplements are especially helpful. These supplements are formulated to provide balanced nutrition with controlled amounts of carbohydrates, along with dietary fiber, protein, and micronutrients, to help with glycemic control and overall metabolic health.
On the other hand, when patients are unable to achieve their nutritional goals by mouth due to certain medical conditions like gastroparesis, which is a common complication of poorly managed diabetes5, tube feeding can become a critical nutritional strategy for diabetic patients.6 Enteral nutrition formulas are designed to meet the specific needs of the diabetic patient by providing that consistent carbohydrate source while also promoting glycemic control. Healthcare professionals must monitor glucose levels closely and adjust tube feeding formulas or regimens as needed.
Other nutritional strategies for diabetes include:
- Dietary Carbohydrate Management: Monitoring and managing total carbohydrate intake, by either counting grams, using the plate method, or looking at the glycemic index of foods. Since carbohydrates have the most significant, immediate impact on blood glucose, it’s important to understand how to manage them.7
- Meal Timing and Consistency: Regular meal patterns and consideration of the timing of carbohydrate consumption, especially in patients on insulin or certain oral medications, can aid in preventing hypo- or hyperglycemia.
- A Balance of Macronutrients: A balanced distribution of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins at meals and snacks may further help support glycemic control.
- Reduction of Added Sugars: Limiting the intake of added sugars is essential for blood glucose management. The American Heart Association recommends that women consume no more than 6 teaspoons or 24 grams of added sugar per day and men stay under 9 teaspoons or 36 grams of added sugar per day.8

Nestlé Health Science offers nutritional solutions for people with diabetes, including oral nutrition supplements and tube-feeding formulas with controlled amounts of carbohydrates and a lower glycemic index that helps maintain normal blood glucose levels. Evidence-based educational resources for both healthcare professionals and patients are also available on our website. Grounded in peer-reviewed research, our nutritional approach aligns with global standards of diabetes care.3
Support Resources
You must be logged in to view all resources.
17 Evidence Found
References
- https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/diabetes.html Last Reviewed: April 24, 2023. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Alison B. Evert, Michelle Dennison, Christopher D. Gardner, W. Timothy Garvey, Ka Hei Karen Lau, Janice MacLeod, Joanna Mitri, Raquel F. Pereira, Kelly Rawlings, Shamera Robinson, Laura Saslow, Sacha Uelmen, Patricia B. Urbanski, William S. Yancy; Nutrition Therapy for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes: A Consensus Report. Diabetes Care 1 May 2019; 42 (5): 731–754. https://doi.org/10.2337/dci19-0014
- ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR et al. on behalf of the American Diabetes Association. Introduction and Methodology: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023 Jan 1;46(Suppl 1):S1-S4.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report website. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html Accessed on August 11, 2023.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Diabetes and Digestion. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/library/features/diabetes-digestion.html Accessed on August 16, 2023.
- Sadiya A. Nutritional therapy for the management of diabetic gastroparesis: clinical review. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2012;5:329-35
- Franz MJ, Boucher JL, Rutten-Ramos S, VanWormer JJ. Lifestyle weight-loss intervention outcomes in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015 Sep;115(9):1447-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2015.02.031. Epub 2015 Apr 29. PMID: 25935570.
- American Heart Association. Added Sugars. Last reviewed: November, 2, 2021. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sugar/added-sugars. Accessed on August 11, 2023.