Abstract Study Summary
The Use of Peptide-Based Diet in Enteral Nutrition Therapy: A Retrospective Cost Analysis
Osman Mohamed Elfadil, MBBS, Ankitaben Patel, MBBS, Raj N. Shah, MBBS, Ryan T. Hurt, MD, PhD, Manpreet S. Mundi, MD
Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2023;47(S2):S18
Helpful Links:
Download the PDF version of this Peptamen Power Pack
Journal Link to Abstract S18: Nutrition and Metabolism Research Oral Paper Session Abstracts (wiley.com)
Background
Home enteral nutrition (HEN) is often used to provide long-term nutrition therapy. Enteral feeding intolerance (EFI) is prevalent in HEN patients and often requires transition to a peptide-based tube feeding formula (PBF).
Objective
Determine the economic impact of using specialized formulas for the treatment of EFI in the HEN population.
Methods
This was a retrospective analysis of the Mayo Clinic Rochester HEN population data, evaluating the cost of transitioning to a 100% whey PBF during therapy from October 2018 through August 2020, with evaluation of demographic data, enteral nutrition (EN) regimen and cost of care being captured through October of 2020 or termination of EN. Cost of care was categorized as follows:
- Emergency Department visits - ED
- Inpatient care - IP
- Outpatient care - OP
- Total cost of care - TC
Results
- 60 patients included
- Mean age 53.5 ± 20.7 years
- 55% female
- Disease Process:
- Malignancy 43.3% - Hepato-biliary/Pancreatic 15.0% - Mucosal Disease 10.0% - Non-Malignant Mechanical Obstruction 8.4% - Bariatric Surgery 8.4% - Gastrointestinal Dysmotility 6.6% - Neurodegenerative/Developmental Delay 6.6% - Functional Disorder 1.7% - Indication for EN included dysphagia/odynophagia, malnutrition, nausea and vomiting, fistula or bowel perforation, inadequate oral intake or obstruction/stricture.
- Pre-transition prevalence of EFI was 43.3%
- Post-transition prevalence of EFI was 21.6%
EN Complications before and after PBF:
| Complications | Pre-Transition % | Post-Transition % |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | 53.3 | 48.3 |
| Tube-Related | 20.0 | 28.3 |
| EFI | 43.3 | 21.6 |
| Metabolic | 3.3 | 10.0 |
Average cost of total care per patient on PBF:
| Last 4 weeks prior to PBF |
First 4 weeks of PBF |
Second 4 weeks of PBF |
|---|---|---|
| $38,744 | $33,944 | $21,129 |
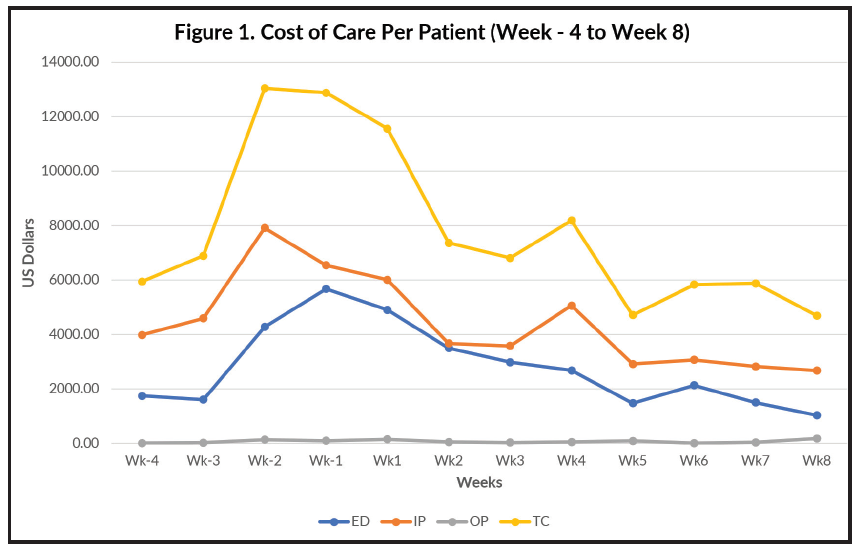
Conclusion
■ Use of 100% whey peptide based formula (PBF) improves enteral feeding intolerance (EFI) and results in a reduction in overall and itemized total cost of care.
Improvements in healthcare resource utilization were seen at all time points up to 8 weeks across multiple diagnoses when patients received Peptamen® formulas as compared to the 4-week period prior to patients receiving Peptamen® formulas.

50.1% reduction in enteral feeding intolerance

45.5% decrease in
cost of care
To request samples and find out more information contact your Nestlé Health Science representative, call 1-800-422-ASK2 (2752), or visit www.NestleMedicalHub.com/brands/peptamen.
Study summary prepared by Nestlé Health Science.
Financial support provided by Nestlé Health Science.
All trademarks are owned by Société des Produits Nestlé S.A., Vevey, Switzerland.
©2024 Nestlé. All rights reserved.
FOR YOUR GI IMPAIRED PATIENTS
whey better
nutrition starts with